In this Article
- What is Prolonged Labour?
- What Are the Causes of Prolonged Labour?
- Signs and Symptoms of Prolonged Labour
- Factors That Can Increase The Risk of Prolonged Labour
- What Happens if Your Labour Seems to Be Going Too Slowly?
- Complications of Prolonged Labour
- How is Prolonged Labour Treated?
- How to Reduce the Risk of Having Prolonged Labour?
The closer D-day gets, the lower is the patience level! There is excitement, happiness and incredible restlessness to meet the little one. Therefore, the thought of the birth being delayed, prolonged or obstructed on D-day is emotionally disheartening.
Prolonged labour can cause serious harm to the baby or the mother and may be life-threatening. Below we shall explore what it is and how it can affect you.
What is Prolonged Labour?
Prolonged Labour is also known as failure to progress or slow progress of labour. When the duration of labour is abnormally more, it is bracketed as prolonged labour. Prolonged labour has no definite definition as at different stages, the delay differs, and the causes also differ.
- Prolonged Early Stage of Labour: When labour prolongs for more than 8 hours without progressing to the first stage.
- Prolonged First Stage of Labour: when labour prolongs for more than 12 hours without progressing into the second stage.
- Prolonged Second Stage of Labour: This usually takes five to thirty minutes. But it is prolonged if it is:
- 2-3 hours for a woman who has been pregnant before.
- 1-2 hours for a woman pregnant for the first time.
So, one is in prolonged labour if the labour lasts more than 20 hours; if its twins or multiples then prolonged labour is declared at 16 hours.
What Are the Causes of Prolonged Labour?
The causes of prolonged labour occur at physical, emotional and social levels. But three principal causes are the 3Ps passage, passenger, and power.
1. Obstructed Labour (Passage)
When the pelvis of the mother is too small, or the passage through which the baby is to come out is small for baby’s head to pass through the labour is prolonged. Rarely, an unusually shaped pelvis or some other obstruction in the passage such as a tumour will also lead to prolonged labour.
2. Foetal factors (Passenger)
The causes are due to the passenger or the fatal. The foetal continues to grow even after the due date, the baby is too big, and the head is too big to pass through the pelvis.
3. Weak Contractions (Power)
One of the major causes of prolonged labour is lack of power in contractions. The contractions are not strong enough to induce pain or able to push for the delivery.
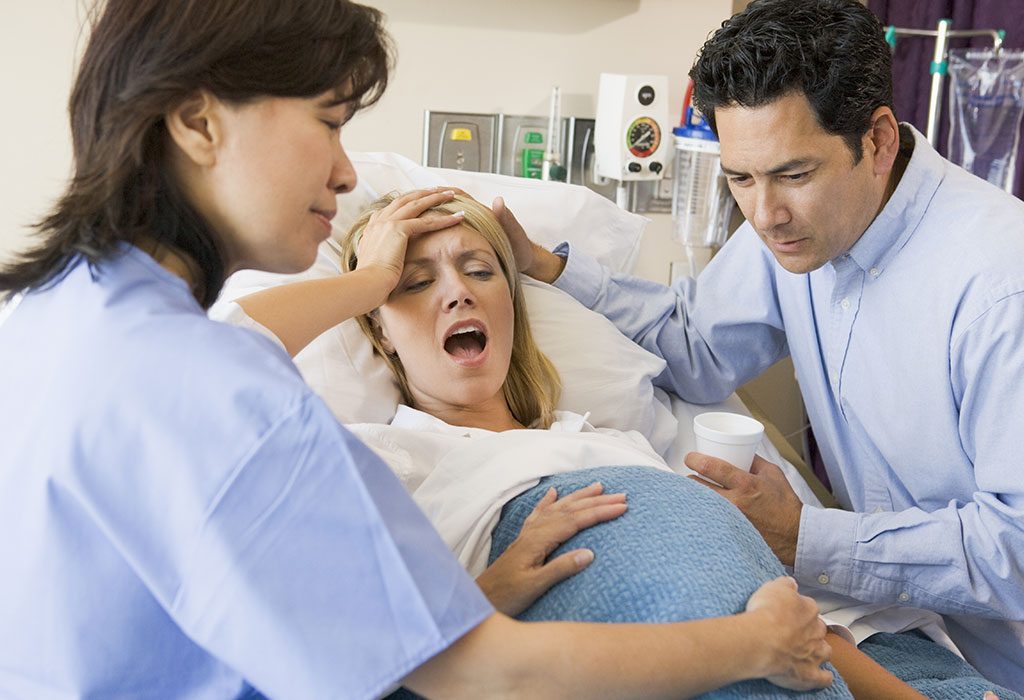

Signs and Symptoms of Prolonged Labour
Signs and symptoms of prolonged labour include :
- Labour beyond 18 hours: the most prominent sign is the delay.
- Maternal exhaustion: The mother’s clear sign of weakness may be a sign to predict prolonged labour
- Other physical symptoms such as unbearable back pain, high pulse rate and a tender uterus also warn of a prolonged labour
- Ketosis: a complication of dehydration, and a lack of carbohydrates (or glucose) for energy in the body. It is the result of the abnormal accumulation of ketone bodies.
Factors That Can Increase The Risk of Prolonged Labour
1. Obesity
Gestational diabetes, pregnancy hypertension accompanied by obesity can increase the size of the baby than the average. Also, such health complications can make the mother weak and the fat around the birth canal can cause problems.
2. Being Too Skinny
Lack of nutrition in the mother leads to lack of nutrition in the foetus and the uterus causing complications to the 3Ps explained above. Hence it is important to take care to be fit and strong. Sometimes a small body would indicate a small pelvis that might delay the baby’s arrival.
3. Decrease in Muscle Mass
One of the causes for the decrease of muscle mass in a pregnant woman is lack of exercises and proactiveness. Labour is a very active and strenuous procedure for the body. It requires good muscle function to progress smoothly through labour, a decrease in muscle mass will reduce strength increasing risk of the slow progress of labour.
4. Advanced Maternal Age or Very Low Maternal Age
The most convenient age group for the body to give birth smoothly is the late teens to the early thirties. Anything before or after is a time that the body is not prepared.
A very young body is not anticipating a birth and hence is not prepared or strong enough to give birth.
Mothers giving birth the first time at an advanced age need to be extremely fit or else, may run into health complications such as gestational diabetes
What Happens if Your Labour Seems to Be Going Too Slowly?
- In the face of slow progress, the only way through this is to stay as calm as possible.
- One of the immediate things done when prolonged labour is recognised is to relax the mother emotionally and mentally, through the presence of a strong companion, pain relief or any other element which may distress the mother.
- One may be given natural or pharmacological pain relief.
- The health team will closely monitor the 3P’s (Power, Passage and Passenger) to understand and take necessary actions to quicken the progress.
- Such tests include continuous foetal monitoring to check baby’s heart rate. An IUPC (Intrauterine Pressure Catheter) to check the power of contractions may also be used.
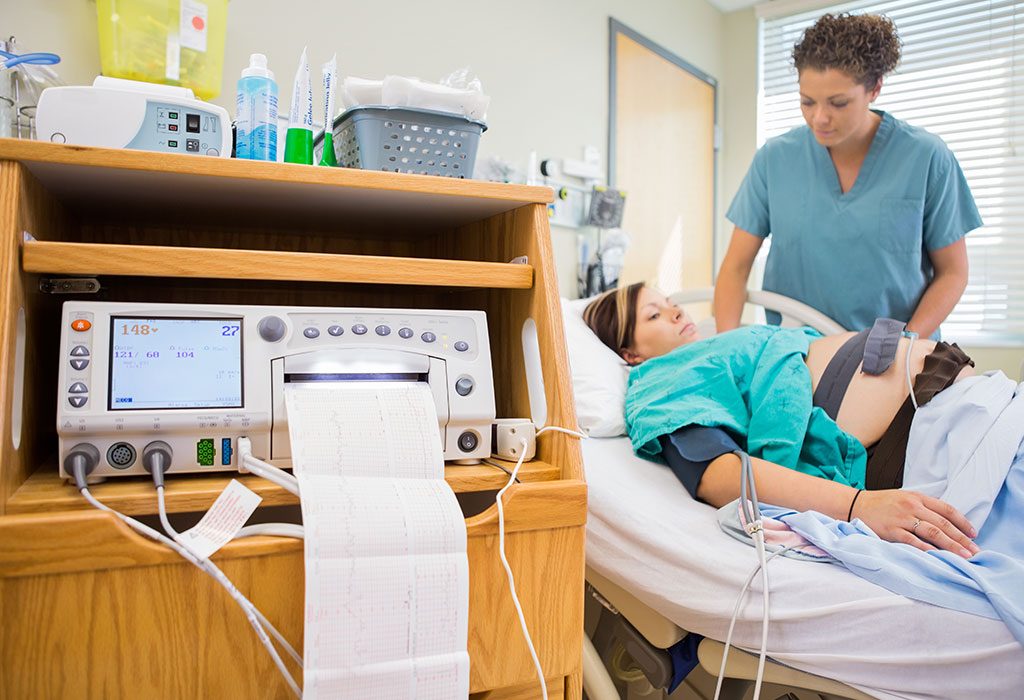
Complications of Prolonged Labour
Prolonged labour can cause serious complications in the mother or the baby. Extreme being the death of the mother or the child. But advanced technology and science have reduced such complications.
Other complications in the mother include:
- Infection
- Uterine Rupture
- Genital Fistulas
Problems for the baby include:
- Infection
- Asphyxia (reduced oxygen to the baby) and traumatic injury
- Stillbirth
How is Prolonged Labour Treated?
The treatment or solution is appropriate ‘prolonged labour management’. This is a medical term that means cautions and precautions taken by the health team to reduce the slow progress of labour:
- Early detection of certain problems during trimesters with the 3Ps and the health of mother will help in progressing towards better fitness.
- Detecting true labour from false labour is one of the first precautions to be observed so as to not induce unnecessary pain and stress.
- Help in inducing labour pains to increase the power of the uterus to push.
- Change in the positioning of the mother to improve the procedure of giving birth more efficiently
- Usage of partogram to record all observations.
- Baby’s heart rate to be monitor hydrate the mother enough to empty the bladder every two hours.
- If certain complications do arise during the natural labour, usage of vacuum extraction to pull out the baby could be used.
- The final solution would be a C section. The doctor might even advice and prepare you during the trimesters for the same.
How to Reduce the Risk of Having Prolonged Labour?
The risk of failure to progress or slow progress of labour could be drastically reduced by the following precautions:
- Healthy Lifestyle: To stay fit and proactive, one has to take care of themselves by maintaining a healthy diet and sticking to an exercise regime.
- Stay Stress-Free: Think about how happy you will be to your baby in your arms. Block out any fears that are there in your heart by thinking only positive thoughts.
A poor lifestyle is the main causes of complications during labour. You can go for regular check-ups so that the obstetrician can spot any issues like obesity or low muscle mass. The power is in your hands and by adopting the right approach, you can minimise prolonged labour.








