In this Article
- What Is Amoxicillin?
- When Do Doctors Prescribe Amoxicillin to Children?
- How to Use Amoxicillin
- Drugs You Should Avoid Using With Amoxicillin
- Amoxicillin Dosage for Kids According to Weight / Age
- What If You Fail to Give a Dose to Your Child?
- What If Your Child Vomits?
- What If You Give an Overdose?
- How to Treat Overdose
- Side Effects of Amoxicillin in Kids
- Safety Measures While Taking Amoxicillin
- Important Things to Remember About Antibiotics
Amoxicillin is a narrow spectrum Penicillin-based antibiotic used for treating bacterial infections. Certified by the world health organisation (WHO) as a very safe drug for children, it is given to treat respiratory infections like whooping cough, sinusitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, and throat and middle ear infections. Some skin infections and urinary tract infections (UTIs) are also treated with this antibiotic, based on the culture results. In this article, we will tell you about the correct dosage of amoxicillin for children.
What Is Amoxicillin?
Amoxicillin is derived from Penicillin, the oldest known antibiotic. It is a better version of its predecessor, the Penicillin, in its ability to tackle a much larger variety of bacterial strains and in its improved ability to get absorbed into the bloodstream. Sold under different brand names, this generic drug called amoxicillin is widely used to treat both gram-negative and gram-positive bacterial infections occurring in the ear, throat, and upper respiratory system.
Amoxicillin, in combination with potassium clavulanate, is a widely used combination that has enhanced absorption characteristics. The clavulanate additive prevents the formation of the bacterial cell wall, thereby broadening the spectrum of bacteria that can be countered with amoxicillin.
When Do Doctors Prescribe Amoxicillin to Children?
Amoxicillin is an antibacterial drug that is used to treat specific strains of bacteria. Contrary to the popular belief, this drug does not work against viral infections such as flu and the common cold, simply because of its targeted mechanism of action against the bacterial cell wall. Some common infections of the ear, nose and throat (ENT) system are effectively treated with amoxicillin. Here is a list of conditions for which doctors usually prescribe amoxicillin for children.

- Acute otitis media, a common type of middle ear infection in children
- Respiratory infections like sinusitis, bronchitis, pneumonia
- A whooping cough
- Throat infections like ‘strep throat’ caused by the streptococcal strain of bacteria
- Tonsillitis
- Some skin infections
- Urinary tract infections
Many parents tend to self-medicate kids with amoxicillin when their child suffers from these conditions recurrently. However, it is a very risky and unhealthy practice to administer antibiotics without consulting a doctor, as the dosage and combination may be specific to specific cases. This not only leads to improper treatment but also paves the way the for development of amoxicillin-resistant bacterial strains in the body.
How to Use Amoxicillin
The generic antibacterial drug called amoxicillin is available under different brand names in the market. It is also available in combination with some chemicals for enhanced action. This medication is very effective and when prescribed to children, they usually get better within two to three days of drug intake. The drug is available in the following forms.
- Oral suspension: Oral suspension is particularly suitable for children. The antibiotic comes as a powder that can be reconstituted in water or milk. It is usually flavoured to enhance its colour and taste. The cleanliness of the diluting ingredients is essential. Usually, a dosing syringe or a measuring cup is used for accurate dilution.
- Paediatric Drops: Paediatric drops are readymade diluted syrups of the desired concentration. They are usually given to small children, where the dosage is very less, and the drug is administered as drops. Paediatric drops come in a bubble gum flavour.
- Capsules: Capsules of amoxicillin are also available with varying doses. They are given to slightly grownup children and usually taken with water, milk or juice.
- Regular Tablets: Amoxicillin is also sold as oral tablets that come with immediate-release (IR) and extended-release (ER). The immediate-release tablets come as generic drugs only. The immediate release and the extended-release tablets differ in their respective rate of drug absorption, and the doctor prescribes the preferred version depending upon the patient’s condition.
- Extended-release Tablets: These tablets are believed to be more effective as they have sustained and elevated doses over long periods.
- Chewable Tablets: Mildly flavoured chewable tablets are available in the market making it easier for children to consume this drug.
The amoxicillin drug in any of the above forms has to be stored in a cool and dry place, away from direct sun, and out of reach of children.
Drugs You Should Avoid Using With Amoxicillin
If the doctor prescribes amoxicillin to your child and your child is already on another medication, you must inform your child’s doctor about the same. There are certain drugs, which when taken along with amoxicillin may have some unwanted and adverse reactions, by way of increased or decreased efficacy of the other drug. The ability of the body to collectively excrete the drugs also matters in deciding treatment options. Some of the drugs that should be avoided are:
- Other anti-bacterial medicines like macrolides, chloramphenicol, tetracycline and sulphonamides
- Probenecid
- Allopurinols
- Warfarin
- Methotrexate, widely used to treat cancer
- Live cholera vaccine
- Venlafaxine
Some parents also give vitamin supplements or herbal medication to their child for other conditions. The doctor should be informed about the same. Although there is no known evidence of an interaction of amoxicillin with vitamins and herbs, it is best to keep the doctor informed.
It is also critical to communicate to the doctor about any known history of allergy to amoxicillin or penicillin, before starting the treatment. If the child is suffering from any kidney disease, asthma or hay fever, the child’s doctor should be aware of it, as this information will be critical in deciding the course of treatment.
Amoxicillin Dosage for Kids According to Weight / Age
The dosage of amoxicillin for kids is very different from that of the adults. Typically, the dosage is determined considering parameters like the age of the child, his or her weight, and the degree and nature of the infection. The table below gives a general guideline for determining the dosages.
| Infection | Age / Weight | Moderate Infection | Severe Infection | ||
| Ear, nose and throat infection | Above 3 months and weight <40 Kgs | 25 mg/kg per day every 12 hours or 20mg/kg per day every 8 hours | 45 mg/kg per day every 12 hours or 40mg/kg per day every 8 hours | ||
| Above 3 months and weight >40 Kgs | 500mg two times a day or 250mg thrice a day | 875mg two times a day or 250mg thrice a day | |||
| Lyme disease | Weight > 40 kg | 500mg to 1g every eight hours for 14 days | 500mg to 2 g every eight hours for 10-30 days | ||
| Weight < 40 kg | 25 to 50mg/kg/day three times a day for 10-21 days | 100mg/kg/day three times a day for 10-30 days | |||
| Streptococcal Pharyngitis | Newborns or babies till 12 weeks age | 2 doses of 30mg/kg per day | |||
| Age more than 12 weeks | 50mg/kg for ten days divided as 2 or 3 doses | ||||
| Otitis Media (Ear Infection) | Age between 4 weeks till 3 months | 20-30mg/kg per day after every twelve hours | |||
| Age 4 months to 12 years | 20-50mg/kg daily after eight to twelve hours | 80-90mg/kg per day divided into 2 doses every twelve hours | |||
| Tonsillitis or Pharyngitis | Age between 1 month and 3 months | 20-30 mg/kg daily taken every twelve hours | |||
| Age 4 months to 12 years | 3 doses of 20-50mg/kg per day every eight to twelve hours | ||||
| Pneumonia | Age above 5 years and weight > 40 kg | 500mg to 1g every eight hours | |||
| Age between 2 months and 5 years and weight < 40 kg | 20 to 90mg/kg/day divided in doses | ||||
| Urinary tract infection | Age > 3 months and weight < 40 kg | 25mg/kg/day divided in doses every 12 hours | 45mg/kg/day divided in doses every 12 hours | ||
| Weight > 40 Kgs | 500mg two times a day or 250mg three times a day | 875mg two times a day | |||
| Skin or Skin Structure Infection | Weight > 40 Kgs | 500mg two times a day or 250mg three times a day | 875mg two times a day or 250mg thrice a day | ||
| Above 3 months and weight >40 Kgs | 25 mg/kg per day every 12 hours or 20mg/kg per day every 8 hours | 45 mg/kg per day every 12 hours or 40mg/kg per day every 8 hours | |||
A fair idea about the permissible dosage is essential in order to avoid giving an overdose to the child. The numbers mentioned above are a general guide to the drug concentrations. The dosage prescribed by the doctor to the specific cases has to be followed diligently.

What If You Fail to Give a Dose to Your Child?
If a dose of amoxicillin is missed, it can be given immediately, provided there is a considerable gap before the next dose. If the time is up for the next dose, then there is no requirement to give a double dosage.
What If Your Child Vomits?
Vomiting is a common side effect of amoxicillin in children. Since the gut microflora is altered by the intake of this drug, it can cause vomiting. Make sure that the kid is taking enough fluids and electrolytes. Usually, consuming food along with the medication helps to control vomiting. Probiotics also help restore the good bacteria in the stomach.
What If You Give an Overdose?
An overdose of the antibiotic may cause intense side effects in children. Depending upon the magnitude of overdose, children may experience severe rashes, kidney damage, nausea, and less urination along with many other symptoms. In such cases, immediate medical treatment is mandatory.
How to Treat Overdose
There is no particular antidote for an amoxicillin overdose in children. To remove the excess amoxicillin from the body, multiple doses of activated charcoal are used. Activated charcoal immediately interrupts the circulation of the antibiotic. Sometimes, doctors wash the stomach to flush out the medicine. Treatment is also given to correct the symptoms arising out of the overdose. Haemodialysis is done in case the condition is severe.
Side Effects of Amoxicillin in Kids
The dosage and frequency of administration vary depending on the severity of the infection and the age of the child. It is advisable to strictly stick to the dosage prescribed by the doctor and finish the full course to avoid the development of an antibiotic-resistant strain of the bacteria. Although considered a very safe drug, amoxicillin may cause some mild side effects in children.
- Stomach discomfort with nausea and mild to severe diarrhoea: This common side effect occurs as a result of changes in the gut flora caused by the antibiotic. If diarrhoea results in considerable loss of body fluids, it is advisable to consult a medical practitioner immediately
- Patches around the mouth, throat and vagina (in girls)
- Sudden swelling of the throat and tongue coupled with difficulty in breathing: This is categorised as ‘anaphylaxis’ or a severe allergic reaction which requires immediate medical attention
- Hives or itchy red patches on the skin
- Loss of appetite
- Tiredness or weakness after taking a dosage of the drug
- General fatigue
- Heavy periods in girls
- Paleness of the skin
- Taste aversion
- Unusual bleeding
- Burning sensation while urinating
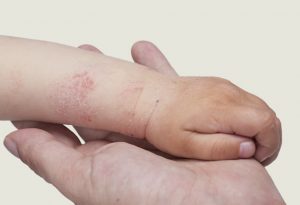
Usually, the side effects subside in a day or two as the child’s body gets acclimatised to the drug, but it is better to keep the doctor informed about any new allergic reaction.
Safety Measures While Taking Amoxicillin
While administering amoxicillin, it is better to consult the doctor and get an opinion on the other allowed medications. Vomiting and diarrhoea are common side effects of antibiotic intake. Do not give medication to stop watery stools without consulting with the doctor.
Also, when a child is treated with amoxicillin, the urine sugar levels may show some false positives. In such cases, other methods of measuring sugar levels can be adopted.
Important Things to Remember About Antibiotics
Some important things that you should remember while taking antibiotics or giving it to your child are mentioned below:
- Strictly follow the dosage and timelines prescribed by the doctor. Increasing or decreasing the dosage can delay the recovery process.
- Complete the course of antibiotic given for an infection. If the medication is stopped in between, it leads to the development of resistant strains of bacteria.
- Watch out for any adverse reactions or side effects, especially in children.
- Avoid any allergic food substances and medicines that have a proven interference with the antibiotic.
Amoxicillin is a safe and effective treatment option for bacterial infections in kids. If your child’s doctor prescribes this drug, give it to your child the right dosage and at the right time. And keep the above pointers in mind to make sure your child recovers completely and feels better soon!









